| CHOUDHURY & GUPTA : INTERCONNECTION PROBLEM IN BANGLADESH |
369 |
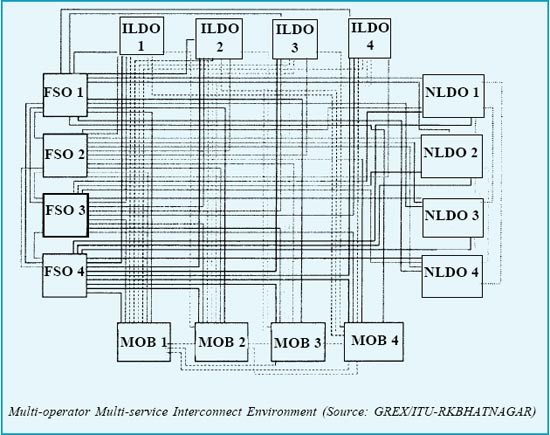
Scenario of Bilateral Interconnection in Multi-service multi- operator environment

4. TECHNOLOGY OPTION FOR EFFICIENT INTERCONNECTION - INTERCONNECT EXCHANGE As can be seen above there will normally be a problem of capacity constraint in the existing switches of incumbent to provide much needed timely interconnection to the new operators. In addition the bilateral interconnection among the service providers is a very inefficient way of interconnection in a multioperator, multi-service scenario. This problem can be tackled by establishment of a common platform for interconnection where all the operators can interconnect. Such an arrangement is commonly known as ‘Interconnect Exchange’ which is described below:- 4.2 The basic concept of the interconnect Exchange is to enable different operators to interconnect at a common point to exchange mutual traffic efficiently. This has been shown in the diagram below: 4.3. The purpose of an Interconnect exchange is to provide a common independent platform for interconnection for mutual traffic exchange & billing and settlement of interconnect usage charges (IUC) for all the existing and future operators in a particular region. |
In order to ensure that this service is non discriminatory, the Interconnect Exchange must be ‘Neutral’ & ‘Autonomous’ and must have the
confidence of both the Regulator and the Operators.
An Interconnect Exchange reduces the numbers of 4.4. The Benefits of an Interconnect Exchange to the Operators The benefits of an Interconnect Exchange to the
|